Artificial intelligence (AI) is set to continue reshaping the electronics manufacturing industry. While some believe it will positively impact worker efficiency, others raise concerns about the unforeseen challenges it may bring. Regardless, change is happening rapidly.
For procurement leaders, AI is proving especially valuable in completing tasks with greater accuracy, efficiency, and speed, enabling them to dedicate more focus to strategic initiatives. By leveraging vast amounts of real-time data, they can effectively mitigate risks, enhance supplier engagement, and stay agile in response to fluctuating market conditions.
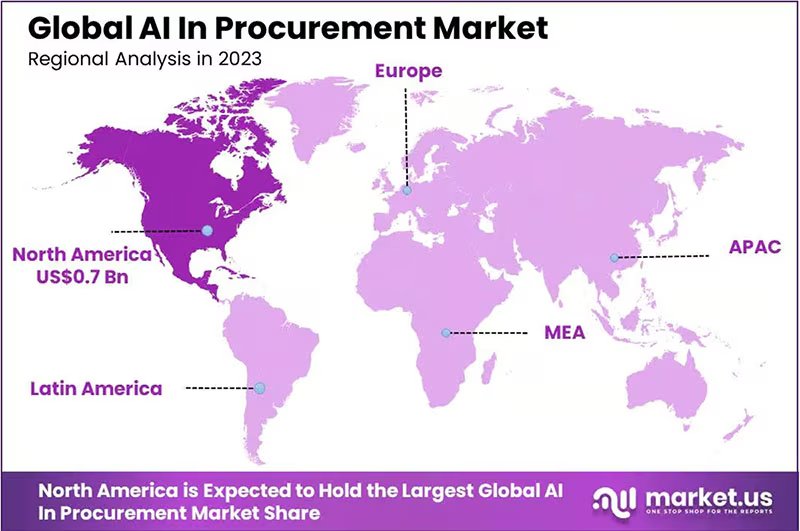
The U.S. Leads in AI Investment for Procurement Globally, the adoption of AI in procurement is expanding swiftly, with its value expected to grow from $1.9 billion in 2023 to $22.6 billion by 2033. This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.1% from 2024 to 2033. In 2023, AI software took a dominant position in the procurement market, making up more than 69.5% of the market share compared to hardware. North America held the largest share, accounting for 38% of the global market in 2023.
1. Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management
One of the most significant applications of AI is in demand forecasting and inventory management. By analyzing large volumes of historical data and market trends, AI can accurately predict future demand fluctuations. This not only helps companies avoid overstocking or stockouts but also optimizes warehousing and logistics, reducing costs and improving efficiency. For example, retail giants like Amazon and Walmart have adopted AI to forecast product demand in different regions, optimizing product distribution plans and inventory allocation.
Moreover, AI can dynamically regulate inventory levels based on real-time data, automatically adjusting replenishment strategies. This fine-tuned management allows supply chains to respond flexibly to rapid market changes, ensuring better supply chain resilience.
2. Automated Procurement and Supplier Management
In procurement, AI is enabling more automation. Traditional procurement processes typically involve manually generating orders, requesting quotes, negotiating, and selecting suppliers. Through natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning technologies, AI can automate these processes. For instance, AI systems can scan supplier quotes, analyze data, and recommend the best procurement decisions, significantly improving procurement efficiency and decision accuracy.
AI also helps businesses manage supplier relationships more effectively. Through data analysis, AI can assess supplier performance, compliance, and potential risks, helping companies make more informed choices. For global companies, AI can optimize supplier networks in complex supply chains, reducing collaboration risks.
3. Risk Management and Supply Chain Optimization
Risk management in supply chains has always been a challenge. Factors such as natural disasters, political instability, and economic fluctuations can have a significant impact on supply chains. AI can monitor and predict potential risks in real-time through machine learning and big data analysis. AI systems can provide data-driven support to help businesses forecast and mitigate risks in the supply chain. For example, when AI detects that a natural disaster may occur in a particular region, it can automatically adjust logistics routes and supply chain arrangements to prevent disruptions.
AI can also optimize supply chains at multiple levels. By tracking real-time data from all stages of the supply chain, AI can identify efficiency bottlenecks, redundant processes, and potential problems, offering suggestions for optimization, thereby reducing waste and improving overall effectiveness.
4. Intelligent Logistics and Transportation Management
Logistics and transportation are key components of the supply chain, and AI is also driving innovation in this area. By integrating autonomous driving, intelligent transportation management systems, and real-time data analysis, AI can enable smarter cargo transportation management. For instance, AI can dynamically adjust transportation routes based on real-time road conditions and weather, optimizing delivery times and costs.
With the development of autonomous driving technologies, AI can also be applied in automated warehouses and distribution centers, reducing labor costs and increasing the speed of sorting, packaging, and delivery. Additionally, AI can predict vehicle maintenance needs by analyzing transportation data, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing the impact of unexpected downtime.
5. Data-Driven Decision Support
Another key advantage of AI is its ability to provide data-driven decision support. In traditional supply chain and procurement decision-making, decision-makers often rely on experience and intuition. In contrast, AI can offer precise predictions and recommendations through deep learning on vast amounts of data. For example, AI can analyze market changes, price fluctuations, and customer feedback to provide procurement personnel with the best times to buy and the optimal purchase quantities. This makes the decision-making process more scientific, rapid, and reliable.
Conclusion
At the same time, AI technology will continue to advance, further enhancing the procurement capabilities of electronics OEMs. For example, Generative AI (GenAI) can learn from vast amounts of data and replicate it to create new content based on prompts or inputs. This could include human language, programming languages, art, chemistry, biology, or any other complex field. According to market research firm Gartner, the most likely advancements to shape procurement operations for professionals are agent reasoning, multimodality, and AI agents.
Agent reasoning in GenAI, as the name implies, enables procurement systems to perform advanced decision-making processes that mimic human cognitive abilities. While complex procurement scenarios may still require human intervention, AI can quickly and accurately analyze data from various sources, allowing for more informed and intelligent decision-making.
Multimodality refers to AI’s ability to integrate and process different types of data (such as text, images, and audio), making GenAI capabilities more intuitive for users. Procurement departments will be able to gather and analyze a wider variety of information, leading to more comprehensive insights and better business strategies.
AI agents automate tasks and make decisions on behalf of humans. These agents can handle basic procurement functions and activities, giving procurement professionals more time to focus on solving problems or handling complex tasks.
While the potential for increased productivity is clear, privacy concerns remain. OEMs must address the evolving data governance and privacy policies and practices to ensure that their AI implementations have proper protections in place. There may be significant activity around this issue in 2025.
As AI continues to develop, it will undoubtedly enhance procurement activities within the supply chain. Soon, machine-driven procurement will become the norm, and procurement teams will be free to focus on the strategic and critical activities within the supply chain.